Google Sheets
Google Sheets is a powerful, web-based spreadsheet application that enables real-time collaboration.
The Google Sheets add-on allows you manage your WordPress posts as Google spreadsheets, transforming how you and your team handles WordPress content.

The add-on
The Google Sheets API is a RESTful interface that lets you read and modify spreadsheets data. This API use the OAuth 2.0 protocol for authentication and authorization. To talk with this API the add-on implements a custom bridge class based on the generic REST bridge that requires OAuth credentials.
A Googe Sheets bridge will synchronize your posts with entries in your Google spreadsheets. Each field of your spreadsheet can be mapped to a post field, post meta or taxonomy term.
With Posts Bridge introspection API you’ll be able to inspect spreadsheet fields to easily map each them to your post fields and taxonomies.
The first row of the table is treated as the column names.
Posts Bridge will read the first row of your spreadsheets looking for column names. If the first row is empty, Posts Bridge will be unable to map spreadsheets rows into WordPress posts.
How to use
The first step to use the add-on is to activate it on the add-ons table on the general settings tab.
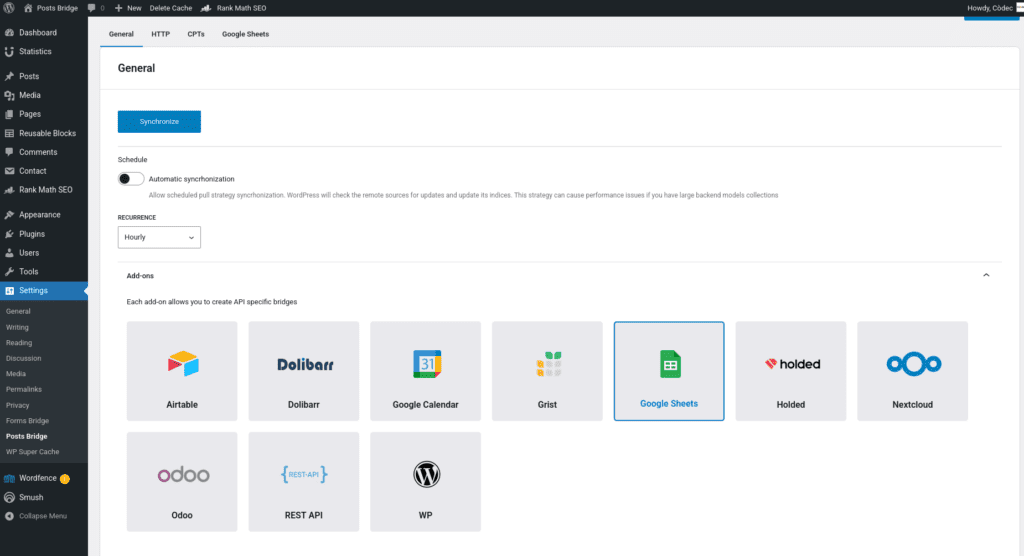
Once activated, a new tab named Google Sheets will be visible in the settings page. If it’s your first time, it should looks like this:
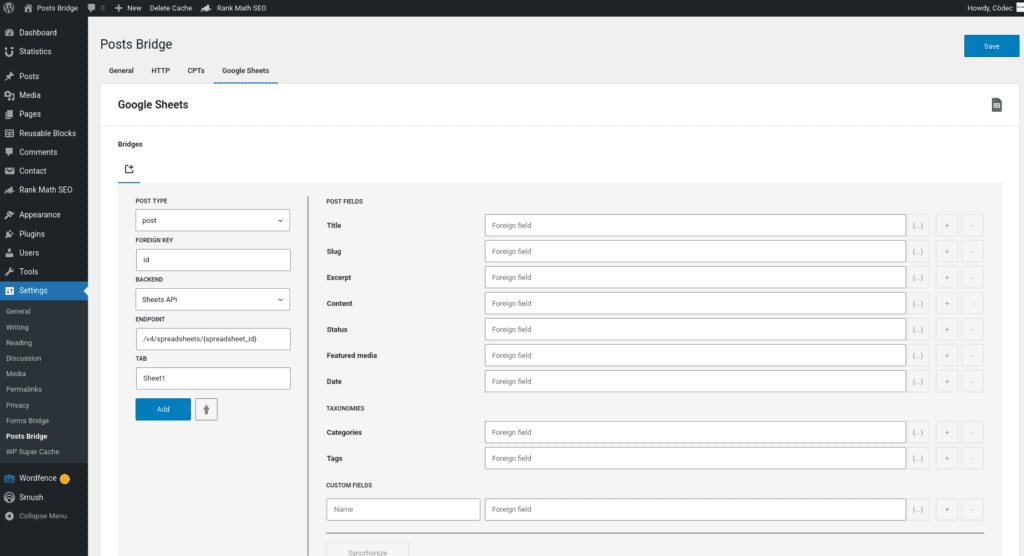
Bridge set up
A Google Sheets bridge will require the following components:
1. Credential
The Sheets API implements the OAuth 2.0 schema to grant access to its resources. To solve this authentication requirement, the add-on requires you to register an OAuth type of credential with the credentials of an Google OAuht Client. Check out our tutorial about How to set up a new OAuth Client on Google Cloud Console.
Once you got the Client ID and Client secret of the Google OAuth client, you have to go to Settings > Posts Bridge > HTTP > Authentication and register a new authentication credential.
Select OAuth as the authentication schema and put the Client ID and Client Secret in the respective fields. For the Authorization URL, you have to set https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2 and for the Scope https://www.googleapis.com/auth/drive.readonly https://www.googleapis.com/auth/spreadsheets.
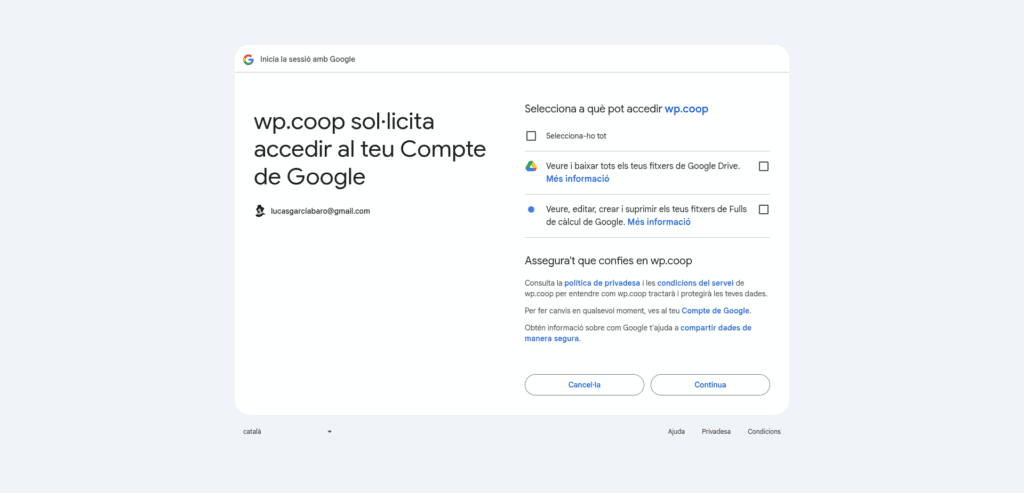
Once registered, Forms Bridge will ask you to Authorize the new credential. Click on the button and a new browser’s tab will be opened asking you for the authorization to Posts Bridge to access your account data. Click on Accept and then you will be redirected again to the HTTP tab of the plugin settings page with your credential authorized.
2. Backend
To configure the Sheets API as a backend, follow this steps:
- Register a new backend with a unique name (Sheets API, for example), and a URL with
https://sheets.googleapis.comas value. - Select
JSONas the Encoding Schema - Select the OAuth credential you’ve configured on the previous step.
3. Post type
Posts Bridge allows you to bridge any registered post type from your WordPress site. If you’ve not registered it yet, you can register it with Posts Bridge. Go to the CPTs tab and create a new custom post type. The registration form will inherit the registration defaults, but you can modify its values at any time. The only required fields are Name, Label and Singular label.
4. Bridge
The add-on’s bridge is an extension of the generic REST bridge with some predefined defaults. Like the REST bridge, the addon’s bridge requires a post type, a foreign key, a backend, and an endpoint. In addition to these standard fields, this kind of bridge will require the tab name you want to use as the source of your bridge data.
The endpoint of a Google Sheets bridge should be like /v4/spreadsheets/${spreadsheet_id}. The spreadsheet ID can be extracted from its URL. For example, the spreadsheet ID in the URL https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/abc1234567/edit#gid=0 is “abc1234567”.
Troubleshooting
To troubleshooting your bridges you can use the plugin’s debug console from the General Settings page. Enable the debug mode and submit a sample form response to see what’s going on under the hood. Take a look to our tutorial about how to use the debug console.
Common issues
- Authentication failures
- Verify OAuth credentials
- Check scope permissions
- Regenerate client secret
- Validate spreadsheet permissions
- If using external audience, check that your project has been verified
- Missing data
- Verify column names
- Check field mapping
- Consider API quotas and potential costs